Experimenting with Redis (DynamoDB)
Sat 25 July 2020Introduction
Recently, I have been exploring NoSQL DBs. During that, I came across DynamoDB.
DynamoDB is a fully managed distributed key-value and document database.
From AWS Documentation:
Amazon DynamoDB is a key-value and document database that delivers single-digit millisecond performance at any scale. It's a fully managed, multiregion, multimaster, durable database with built-in security, backup and restore, and in-memory caching for internet-scale applications. DynamoDB can handle more than 10 trillion requests per day and can support peaks of more than 20 million requests per second.
In DynamoDB
- Data is stored as a collection of documents in tables.
- Documents are stored across the nodes in a cluster. Partition key's value is used to determine the node, in which the document has to be stored.
- Each document can also have a sort key which can be used to store the documents in sorted order based on the value of that key.
- Data cannot be queried without knowing the value of partition key in the document.
- Data can also be queried by using combination of partition key and sort key.
- Combination of partition key and sort key needs to be unique.
Let us consider an example of managing movies catalog in DynamoDB to understand the above mentioned facts. The catalog consists of multiple entries with details about category, title, release year of the movie.
{
"category": "scifi",
"year": "1999",
"title": "The Matrix"
}
Our intention is to store and query them based on category and release year.
To Achieve that, we might store something similar to the following document in table movies.
{
"partition_key": "category:scifi",
"sort_key": "year:1996",
"title": "The Matrix"
}
To get all the movies that belong to a particular category, we have to query the catalog using the partition key . To get all the movies released in a particular year, in a particular category, we can use the combination of sort key and partition key to query the catalog.
The above mentioned facts about DynamoDB, made me think about an experiment - Can I build something that mimics these using Redis
About Redis from redis.io
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache and message broker. It supports data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs, geospatial indexes with radius queries and streams.
Redis supports sharding data based on keys, It supports data types hashes, sortedset. One important feature that made me interested is the ability to read the members in sorted set using the command ZRANGEBYLEX
How to implement this
My first thought about how to store the documents was simple. It was create to a value using partition key, sort key and a json dump which had other fields from the document and store it in a sorted set with score as 0, so all I have to do now is to use ZRANGEBYLEX to provide the querying capabilities that I mentioned above.
For example, In a table movies, if the document that needed to be stored is
{
"partition_key": "category:scifi",
"sort_key": "year:1999",
"title": "The Matrix"
}
I can form category:scifi|year:1999|"{\"title\": \"The Matrix\"}" and store it in a sortedset movies.
Problem with this approach
Storing the data like this can only support range queries. It cannot support get item query using the combination of partition key and sort key, also it cannot support updating / deleting a value by using partition key and sort key.
Solving the Get Item and Delete Item
I decided to use hash for storing the values, instead of having it as a part of the sort key. When we have to store document,
{
"partition_key": "category:scifi",
"sort_key": "year:1999",
"title": "The Matrix"
}
There will two parts that needs to be stored
category:scifi|year:1999 in movies__sortedset sortedset
"{\"title\": \"The Matrix\"}" in a hash with key category:scifi|year:1999 in movies__hashmap
The sorted set can act as an Index to help with range queries. The hash table can be used for get, delete queries.
Distributing the data according to the partition key
Both the value in hashmap and value in the sorted set needs to be present in the same node. For this requirement I decided to use {}. Using these braces, will make redis to consider the values present within these braces for distributing the data among the nodes.
From redis documentation - https://redis.io/topics/cluster-spec
If the key contains a "{...}" pattern only the substring between { and } is hashed in order to obtain the hash slot.
Keeping with same example,
{
"partition_key": "category:scifi",
"sort_key": "year:1999",
"title": "The Matrix"
}
I decided to have a hash table and sortedset per partition key, so the hash map name will be movies__{<partition_key>}__hashmap and movies__{<partition>}__sortedset.
Inside those hash table and sortedset I would have stored those values as I mentioned above.
Implementation
I implemented this using docker (for creating a redis cluster) and python. Using docker-compose, I created a redis cluster (3 masters and 3 slaves), then I created another python container, in which I added to the script to implement the read the data and to store the data. I also added support for range queries (query using partition key and sort range).
Then I used pytest to test positive / success workflows. I don't want to go into details about the test cases that I have written, you can find the code here.
To test the distribution of partition and sort keys among the nodes, I downloaded IMDB Dataset, in that title dataset had similar structure as mentioned in the above example.
Example
{
"region": "US",
"title": "The Clown and His Dogs",
"titleId": "tt0000002"
}
In this I used region for partition key and titleId for sort key
I loaded the first 100k documents from this dataset using a python script - movies client to a table movies. It took around 12 minutes on my machine.
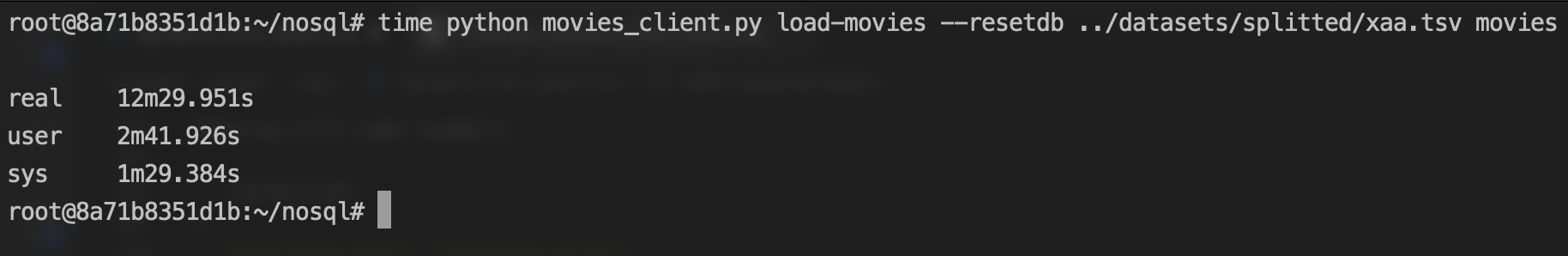
Then, I used the key command's output in redis nodes to list the keys stored in them. I found that both the hash table values and ordered set values of the same partition key to be in the same master node using key command's output.
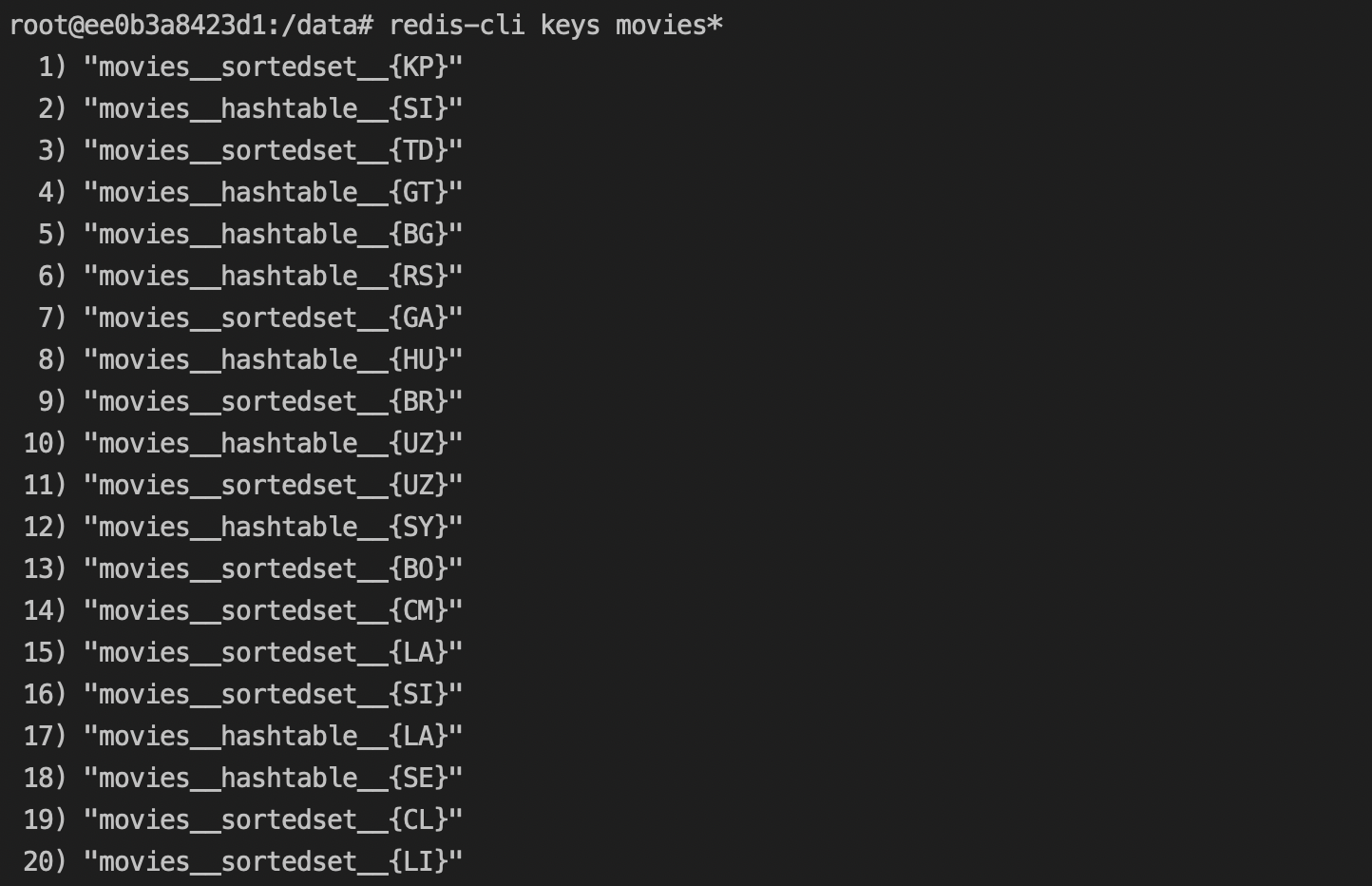
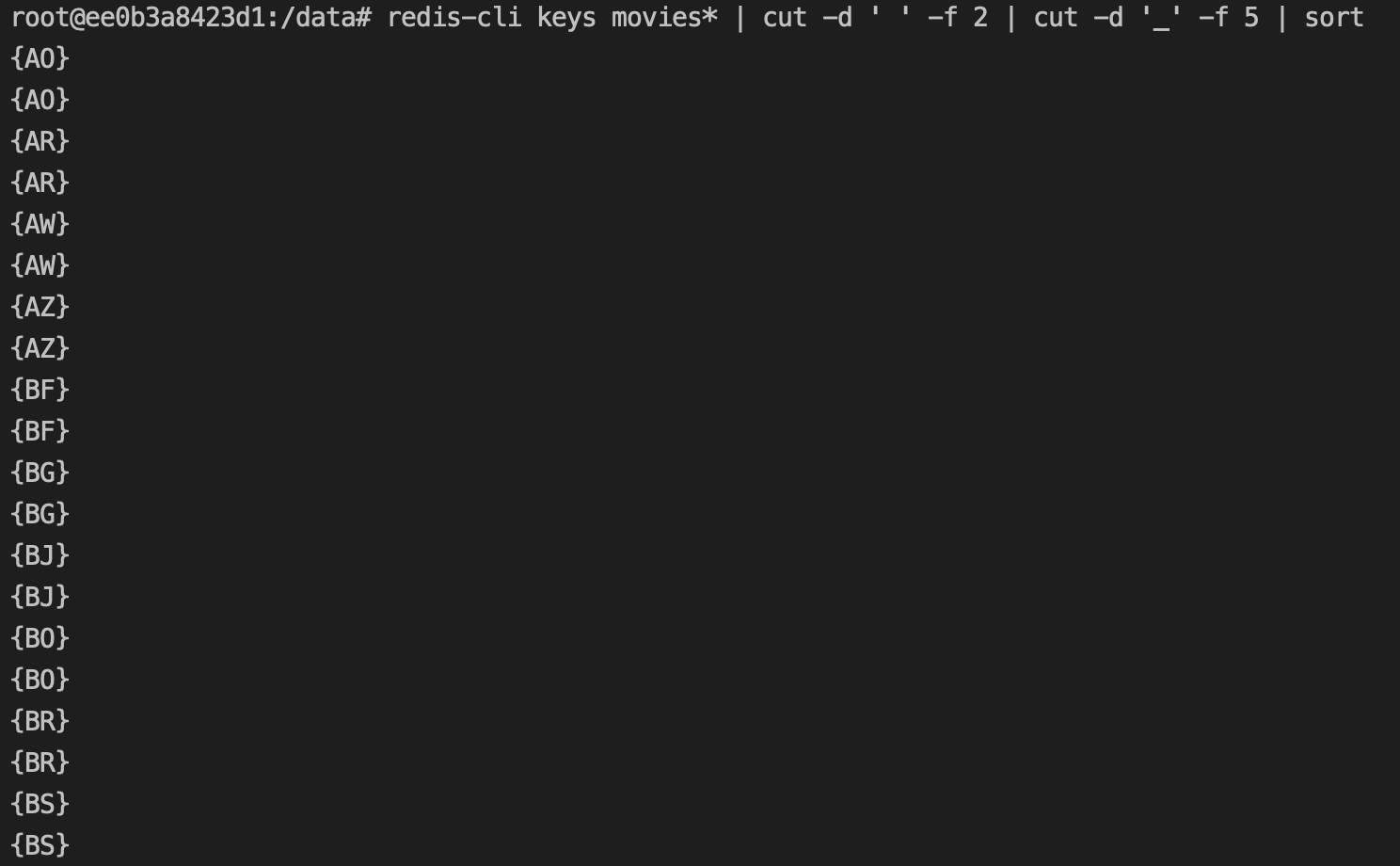
To find out about the performance during querying using partition key and sort key. I wrote a script to query the table using partition key (Region) and sort range (Range of titleId)
The output of getting movie details in US Region ranging from titleId 1 to 10000 in 10 batches (batch size - 1000) took 0.2 seconds
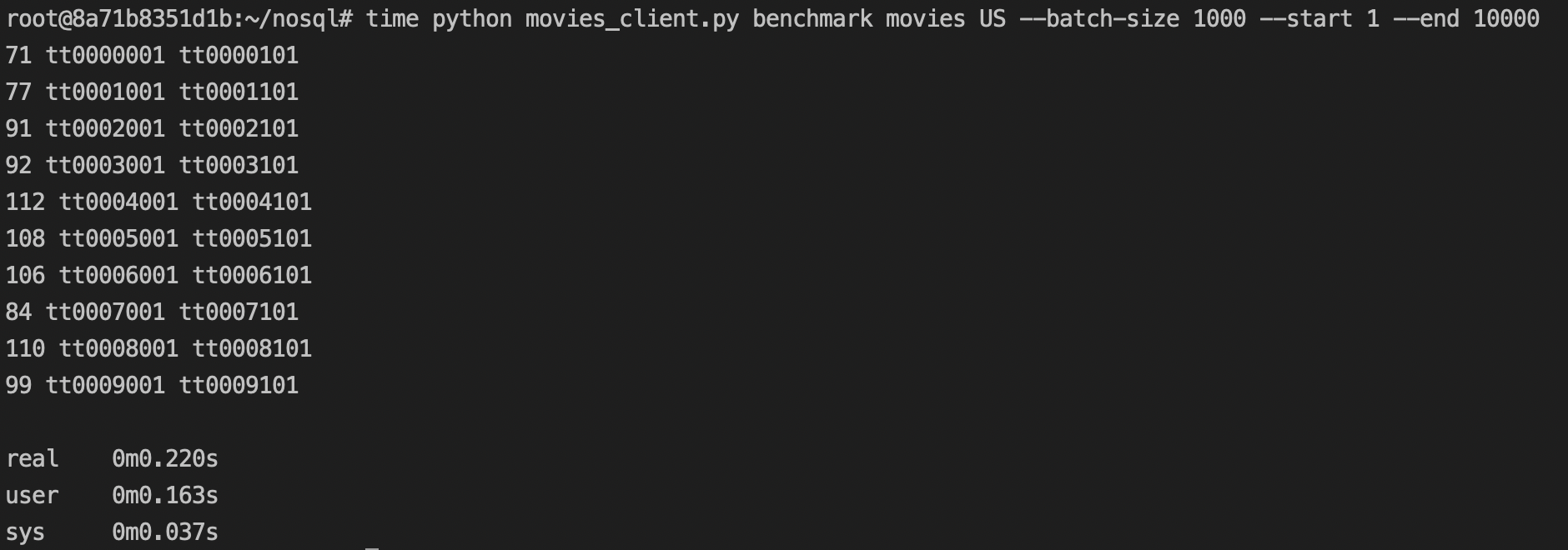
Note: The above is just an indication of the performance of this implementation, it is not for benchmarking against Dynamodb. I never intended this implementation to be benchmarked against DynamoDB
Conclusion
In this, I just verified whether it is possible to build something like dynamodb on top of redis (by me). I never intended this to be an alternative to DynamoDB. This is no way near the capabilities of DynamoDB. Few things that are not sure about this is 1. What will happen if the memory of a node is full. 2. Does storing the hash and sortedset has any advantage?
I just thought it would be an interesting experiment to create such a data store for fun. I have the code here.